- Splay 树
- 前言
- 简介
- 需要维护的信息
- 操作
- 基本操作
- 旋转操作
- Splay 操作
- 插入操作
- 查询排名为 k 的数
- 查询前驱
- 查询后继
- 合并两棵 Splay 树
- 删除节点操作
- 完整代码
- PS
Splay 树
前言
本文是我学习 Splay 树的笔记, 学习时以及写下此笔记时大量参考了写得非常好的 OI-Wiki 的文章, 包括一些配图也直接偷懒拿的文内配图, 轻喷(bushi
当然还是有一些我自己的理解, 希望能帮到你.
简介
Splay 树又称伸展树, 是二叉搜索树中的一种, 通过将节点旋转到根节点的 Splay 操作, 使得整棵树在满足二叉搜索树的性质的同时保持平衡, 不至于退化成链.
需要维护的信息
| 根节点编号 | 节点总数 | 节点的父亲编号 | 节点的左右儿子编号 | 节点权值 | 权值出现次数 | 子树大小 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
root |
total |
father[i] |
child[i][2] |
value[i] |
count[i] |
size[i] |
操作
基本操作
void maintain(x): 在对节点进行修改后更新节点x的子树大小;bool get(x): 判断一个节点是其父亲的左孩子还是右孩子;void clear(x): 删除一个节点的信息.
代码如下:
int root = 0, total = 0, father[maxN] = {}, child[maxN][2] = {}, value[maxN] = {}, count[maxN] = {}, size[maxN] = {};
void maintain(int x) {
size[x] = size[child[x][0]] + size[child[x][1]] + count[x];
}
bool get(int x) {
return x == child[father[x]][1];
}
void clear(int x) {
child[x][0] = child[x][1] = father[x] = value[x] = count[x] = 0;
}
旋转操作
旋转操作是为了将一个节点的位置与其父亲交换从而上升而不破坏二叉搜索树的性质. 一个节点要上升位置需要进行左旋还是右旋取决于这个节点是其父亲的左孩子还是右孩子: 如果是左孩子, 则进行右旋; 反之, 则进行左旋.
下面给出左旋和右旋的图示以辅助理解:
如上图所示, 左边以节点 1 为根的树在节点 2 右旋后转化成了右边以 2 为根的树, 通过图示我们可以得出以下的右旋具体步骤 (设要旋转的节点为 x, 其父亲为 y):
-
如果
x有右儿子, 将x的右儿子分配为y的左儿子并其父亲设置为y.if (child[x][1]) { child[y][0] = child[x][1]; father[child[y][0]] = y; } -
将
x的父亲设置为y的父亲并将y在原先父亲的位置设置为x(如果y是根节点, 则x的父亲被设置为 0, 即不存在); 若y不是根节点, 则将y在原先父亲处的位置设置为x.father[x] = father[y]; if (father[y]) child[father[y]][get(y)] = x; -
将
x的右儿子设置为y, 并将y的父亲设置为x.father[y] = x;
这样就完成了右旋操作, 同样的, 我们可以效仿右旋操作得到左旋操作的方法, 代码如下:
if (child[x][0]) {
child[y][1] = child[x][0];
father[child[y][1]] = y;
}
father[x] = father[y];
child[x][0] = y;
if (father[y])
child[father[y]][get(y)] = x;
father[y] = x;
然而要理解左旋或者右旋的操作的具体原因, 答案还要从二叉搜索树的最基本性质上找.
旋转操作的本质是让被旋转的节点与其父亲交换从而使得被旋转节点的位置上升, 那么从交换后的位置开始考虑 (以上图左边的树为例, 节点间大小关系不变):
由于在原先的树中, 节点 2 是节点 1 的左儿子, 因此可以得到 Node(2) < Node(1), 因此旋转后节点 1 与节点 2 调换, 节点 1 应为节点 2 的右孩子, 如下图:
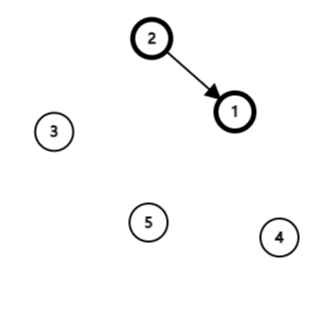
由于节点 4 在原先的树中是最小的节点, 节点 3 在原先的树中是最大的节点, 因此节点 4 和节点 3 的位置是确定的, 并且旋转操作不涉及它们的子树, 据此我们可以得到下图:
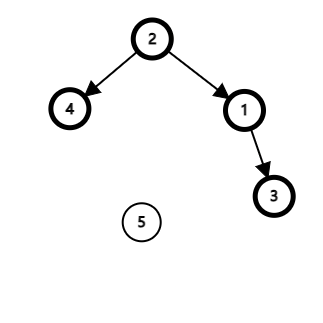
这个不难理解, 因为节点 4 在原先的树中是最小的节点, 因此节点 4 在旋转后同样应该是树中最小的节点, 则将其放到节点 1 的左孩子位置, 而这个过程不会影响节点 4 的子树; 节点 3 同理.
剩下节点 5 没有分配, 我们回到原先的树中观察其数量关系, 可以得到节点 5 在节点 1 的左子树中且是节点 2 的右孩子, 则有 Node(2) < Node(5)<Node(1). 因此, 节点 5 的位置应在节点 2 的右子树且在节点 1 的左子树, 那么它的位置就很明显了:
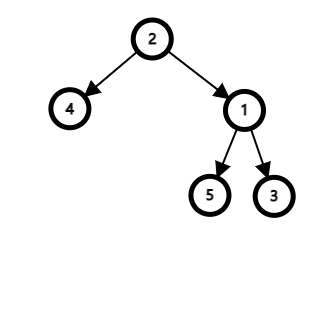
这样我们就完成了右旋操作, 左旋操作同样可以效仿上面的分析过程得出, 不再赘述.
实际上通过观察左旋和右旋操作中的数量关系, 我们可以将左旋操作和右旋操作简化成一份代码, 代码如下:
int y = father[x], isRight = get(x);
child[y][isRight] = child[x][isRight ^ 1];
if (child[x][isRight ^ 1])
father[child[x][isRight ^ 1]] = y;
father[x] = father[y];
child[x][isRight ^ 1] = y;
if (father[y])
child[father[y]][get(y)] = x;
father[y] = x;
maintain(y);
maintain(x);
//maintain(x)可忽略, 因为我们是自底向上进行Splay操作的, 这意味着第一次进行rotate操作时的x是被修改的节点.
//而被修改的节点的信息一定是最新的, 不需要被更新, 因此这一步可忽略.
解决了 rotate 操作后, 接下来我们就要开始研究 Splay 操作了.
Splay 操作
Splay 树与其他平衡树相比特点就是其名字中的 Splay 操作, Splay 树要求每访问一次一个节点, 应将其旋至根上以保持平衡. 有了上述 rotate 操作的实现之后, 我们只需要调用写好的函数即可. 下面我们来讨论一个节点 x 进行 Splay 操作的三种可能情况:
-
x的父亲是根节点, 此时直接rotate(x)即可; -
x的父亲不是根节点, 且两者位于同一侧 (即均是各自父亲的左孩子或右孩子), 则先rotate(y), 再rotate(x); -
x的父亲不是根节点, 且两者不在同一侧 (即x是y的左孩子而y是其父亲的右孩子或反之), 则执行rotate(x)两次即可;
重复上述步骤直到 x 已经是根节点 (没有父亲) 为止. 代码如下:
void splay(int x) {
for (int i = father[x]; i; rotate(x), i = father[x])
if (father[i])
rotate(get(x) == get(i) ? i : x);
root = x;
}
有了这两个关键操作之后, 接下来的基本操作就可以借助这两个操作按部就班地实现即可~
插入操作
要插入一个节点, 我们先进行一次查询操作:
- 如果树是空的, 则直接插入到根节点中;
- 如果树中已有待插入的值, 则将其出现次数加一,并更新子树大小;
- 如果树中不存在待插入的值, 此时查询指针将指向一个空节点, 这个点就是我们要插入的位置, 插入后更新子树大小;
完成操作之后切记进行 Splay 操作! 代码如下:
void insert(int x) {
//如果树空
if (not root) {
value[++total] = x;
++count[total];
root = total;
maintain(root);
//不需要Splay操作, 因为此时只有根节点.
return;
}
//如果树非空, 则从根节点进行查询, 用两个变量记录当前查找到的节点及其父亲.
int cursor = root, fa = 0;
while (true) {
//如果树中已有待插入的值, 则将出现次数加一, 更新子树大小并进行Splay操作.
if (value[cursor] == x) {
++count[cursor];
maintain(cursor);
maintain(fa);
splay(cursor);
break;
}
//否则接着查询.
fa = cursor;
cursor = child[cursor][x > value[cursor]];
//如果进入了一个空节点, 说明树中不存在待插入的值.
//则新建一个节点, 更新子树大小并进行Splay操作.
if (not cursor) {
value[++total] = x;
++count[total];
child[fa][x > value[fa]] = total;
father[total] = fa;
maintain(total);
maintain(fa);
splay(total);
break;
}
}
}
查询排名为 k 的数
设 k 为剩余排名, 具体步骤如下:
- 如果左子树非空且剩余排名 k 不大于左子树的大小, 那么向左子树查找.
- 否则将 k 减去左子树的和根的大小. 如果此时 k 的值小于等于 0, 则返回根节点的权值; 否则继续向右子树查找.
int getByRank(int rank) {
int cursor = root;
while (true) {
if (child[cursor][0] and rank <= size[child[cursor][0]]) {
cursor = child[cursor][0];
} else {
rank -= size[child[cursor][0]] + count[cursor];
if (rank <= 0) {
splay(cursor);
return value[cursor];
}
cursor = child[cursor][1];
}
}
}
查询前驱
前驱定义为小于 x 的最大的数, 那么查询前驱可以转化为: 将 x 插入 (此时 x 已经在根的位置了), 前驱即为 x 的左子树中最右边的节点, 最后将 x 删除即可.
int pre() {
int cursor = child[root][0];
if (not cursor)
return cursor;
while (child[cursor][1])
cursor = child[cursor][1];
splay(cursor);
return cursor;
}
查询后继
后继定义为大于 x 的最小的数, 查询方法和前驱类似: x 的右子树中最左边的节点.
int nxt() {
int cursor = child[root][1];
if (not cursor)
return cursor;
while (child[cursor][0])
cursor = child[cursor][0];
splay(cursor);
return cursor;
}
注: 这里提及的查询前驱和后继的函数并不是完整的操作, 这里的两个函数的调用时机是待查询的节点已经是根节点之后. 因此, 查询前应使用某种方法将其旋至根节点, 如果待查询的数不在树中, 还应将其插入, 查询完毕后将其删除, 如:
insert(x);
cout << value[pre()] << endl;
remove(x);
insert(x);
cout << value[nxt()] << endl;
remove(x);
合并两棵 Splay 树
这听起来是个特殊的需求, 实际上这是作为删除节点操作的前置要求提出的. 这里我们给要合并的两棵树提出的条件是其中一棵树的最大值应小于另一颗树的最小值.
有了这样的条件, 我们不难得出合并两棵树的操作, 即将数值较大的那棵树分配到数值较小的那棵树中的最大值的右孩子处, 这样便能保证二叉平衡树的性质, 当然反过来也是可以的.
删除节点操作
有了上面提到的合并方法, 我们具体应该如何删除一个节点呢? 假设待删除的节点为 x, 如果我们把它旋至根, 不难发现此时待删除的节点的左右子树恰好符合上述条件. 因此我们将节点删除后按照上述方法合并左右子树即可.
void remove(int x) {
rank(x);
if (count[root] > 1) {
--count[root];
maintain(root);
return;
}
if (not child[root][0] and not child[root][1]) {
clear(root);
root = 0;
return;
}
if (not child[root][0]) {
int cur = root;
root = child[root][1];
father[root] = 0;
clear(cur);
return;
}
if (not child[root][1]) {
int cur = root;
root = child[root][0];
father[root] = 0;
clear(cur);
return;
}
int cur = root, k = pre();
father[child[cur][1]] = k;
child[k][1] = child[cur][1];
clear(cur);
maintain(root);
}
完整代码
自此, Splay 树已经被我们完整实现了, 不妨到洛谷的模板题尝试一下你的代码吧. 完整代码如下:
namespace Splay {
int root = 0, total = 0, father[maxN] = {}, child[maxN][2] = {}, value[maxN] = {}, count[maxN] = {}, size[maxN] = {};
void maintain(int x) {
size[x] = size[child[x][0]] + size[child[x][1]] + count[x];
}
bool get(int x) {
return x == child[father[x]][1];
}
void clear(int x) {
child[x][0] = child[x][1] = father[x] = value[x] = count[x] = 0;
}
void rotate(int x) {
int y = father[x], isRight = get(x);
/*
//如果x是y的左儿子
if (not isRight) {
//如果有x的右儿子, 则将x的右儿子分配给y为左儿子
if (child[x][1]) {
//将y的左儿子设置为x的右儿子
child[y][0] = child[x][1];
//将x的右儿子的父亲设置为y
father[child[y][0]] = y;
}
//将x的父亲设置为y的父亲
father[x] = father[y];
//将x的右儿子设置为y
child[x][1] = y;
//如果y有父亲, 则将y原先的位置设置为x
if (father[y])
child[father[y]][get(y)] = x;
//将y的父亲设置为x
father[y] = x;
} else {
//如果x有左儿子, 则将x的左儿子分配给y为右儿子
if (child[x][0]) {
//将y的右儿子设置为x的左儿子
child[y][1] = child[x][0];
//将y的右儿子的父亲设置为y
father[child[y][1]] = y;
}
//将x的父亲设置为y的父亲
father[x] = father[y];
//将x的左儿子设置为y
child[x][0] = y;
//如果y有父亲, 则将y原先的位置设置为x
if (father[y])
child[father[y]][get(y)] = x;
//将y的父亲设置为x
father[y] = x;
}
*/
/**
* 由于当x是y的左儿子时, x的相反方向(即右)的儿子一定分配给y做同方向(即左)的儿子, y一定分配给x做反方向(即右)的儿子, 反之同理, 因此上述代码可以简化为下面的代码.
* 实际上上面的四个方向(左右左右)反映了二叉搜索树中的大小关系(一个节点的左子树均比该节点小, 反之均比该节点大), 以x是y的左儿子为例:
* x是y的左儿子, 因此x所在的子树的所有节点都比y小, 则x的右儿子也一定比y小;
* 所以当y右旋下来时, x的右儿子`比y小, 因而分配给y作为左儿子;
* 又因为x是y的左儿子, 所以x比y小, 也就是说y比x大;
* 因此y右旋下来作为x的左儿子时, 一定处于比x大的右边, 即作为x的右儿子.
* 当y是x的右儿子时同理.
*/
child[y][isRight] = child[x][isRight ^ 1];
if (child[x][isRight ^ 1])
father[child[x][isRight ^ 1]] = y;
father[x] = father[y];
child[x][isRight ^ 1] = y;
if (father[y])
child[father[y]][get(y)] = x;
father[y] = x;
maintain(y);
maintain(x);
}
void splay(int x) {
for (int i = father[x]; i; rotate(x), i = father[x])
if (father[i])
rotate(get(x) == get(i) ? i : x);
root = x;
}
void insert(int x) {
if (not root) {
value[++total] = x;
++count[total];
root = total;
maintain(root);
return;
}
int cursor = root, fa = 0;
while (true) {
if (value[cursor] == x) {
++count[cursor];
maintain(cursor);
maintain(fa);
splay(cursor);
break;
}
fa = cursor;
cursor = child[cursor][x > value[cursor]];
if (not cursor) {
value[++total] = x;
++count[total];
child[fa][x > value[fa]] = total;
father[total] = fa;
maintain(total);
maintain(fa);
splay(total);
break;
}
}
}
int rank(int x) {
int ans = 0, cursor = root;
while (true) {
if (value[cursor] > x) {
cursor = child[cursor][0];
} else {
ans += size[child[cursor][0]];
if (value[cursor] == x) {
splay(cursor);
return ans + 1;
}
ans += count[cursor];
cursor = child[cursor][1];
}
}
}
int getByRank(int rank) {
int cursor = root;
while (true) {
if (child[cursor][0] and rank <= size[child[cursor][0]]) {
cursor = child[cursor][0];
} else {
rank -= size[child[cursor][0]] + count[cursor];
if (rank <= 0) {
splay(cursor);
return value[cursor];
}
cursor = child[cursor][1];
}
}
}
int pre() {
int cursor = child[root][0];
if (not cursor)
return cursor;
while (child[cursor][1])
cursor = child[cursor][1];
splay(cursor);
return cursor;
}
int nxt() {
int cursor = child[root][1];
if (not cursor)
return cursor;
while (child[cursor][0])
cursor = child[cursor][0];
splay(cursor);
return cursor;
}
void remove(int x) {
rank(x);
if (count[root] > 1) {
--count[root];
maintain(root);
return;
}
if (not child[root][0] and not child[root][1]) {
clear(root);
root = 0;
return;
}
if (not child[root][0]) {
int cur = root;
root = child[root][1];
father[root] = 0;
clear(cur);
return;
}
if (not child[root][1]) {
int cur = root;
root = child[root][0];
father[root] = 0;
clear(cur);
return;
}
int cur = root, k = pre();
father[child[cur][1]] = k;
child[k][1] = child[cur][1];
clear(cur);
maintain(root);
}
}
PS
- 实际上想起来要学还是因为同学让我帮忙梳理数据结构知识的请求, 学完还蛮爽的(
AVL的笔记考完试再说吧! 也许也会写一遍, 或许不会, 再说吧~






